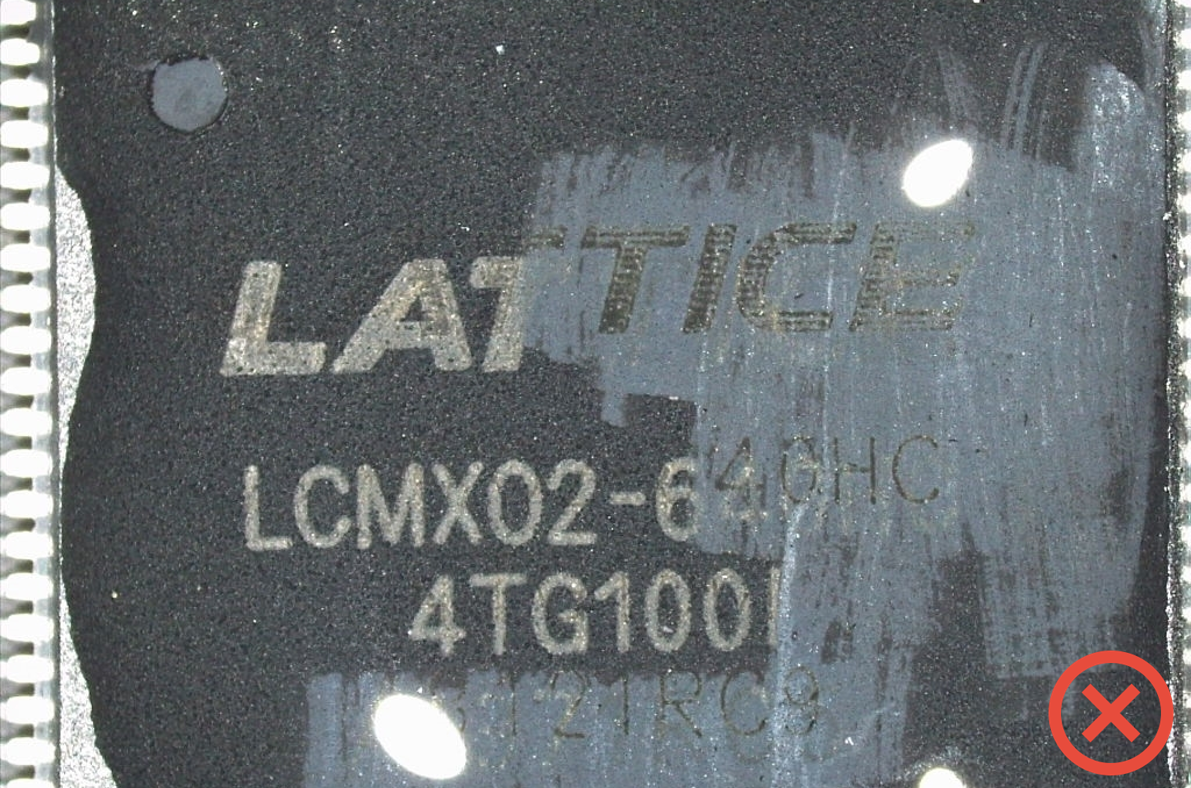Verifying the authenticity of components or their homogeneity within a batch is a major challenge today. Particularly when you're sourcing them from new intermediaries, or from older batches (integrity after long-term storage).
The testing protocol applied by ELEMCA complies with current standards:
- IDEA-STD-1010: Acceptability criteria. Acceptability of Electronic Components Distributed in the Open Market
- AS6171A and or ISO 2859-1: inspection methods and sampling rules (number of components to be analyzed according to the size of the batch supplied).
The aim of these checks is to assess the conformity of the components under test with regard to their expected characteristics: external visual appearance of the package and terminations, dimensions and integrity of the chip, bondings and leadframe, electrical functions, pin wettability.
Our verifications are based on an extensive ELEMCA database of findings on both genuine components and proven counterfeits.
The techniques we use are adapted to the suspected level of counterfeit refinement, as well as to the criticality and technology of the component.
Non destructive testing
Destructive analyses
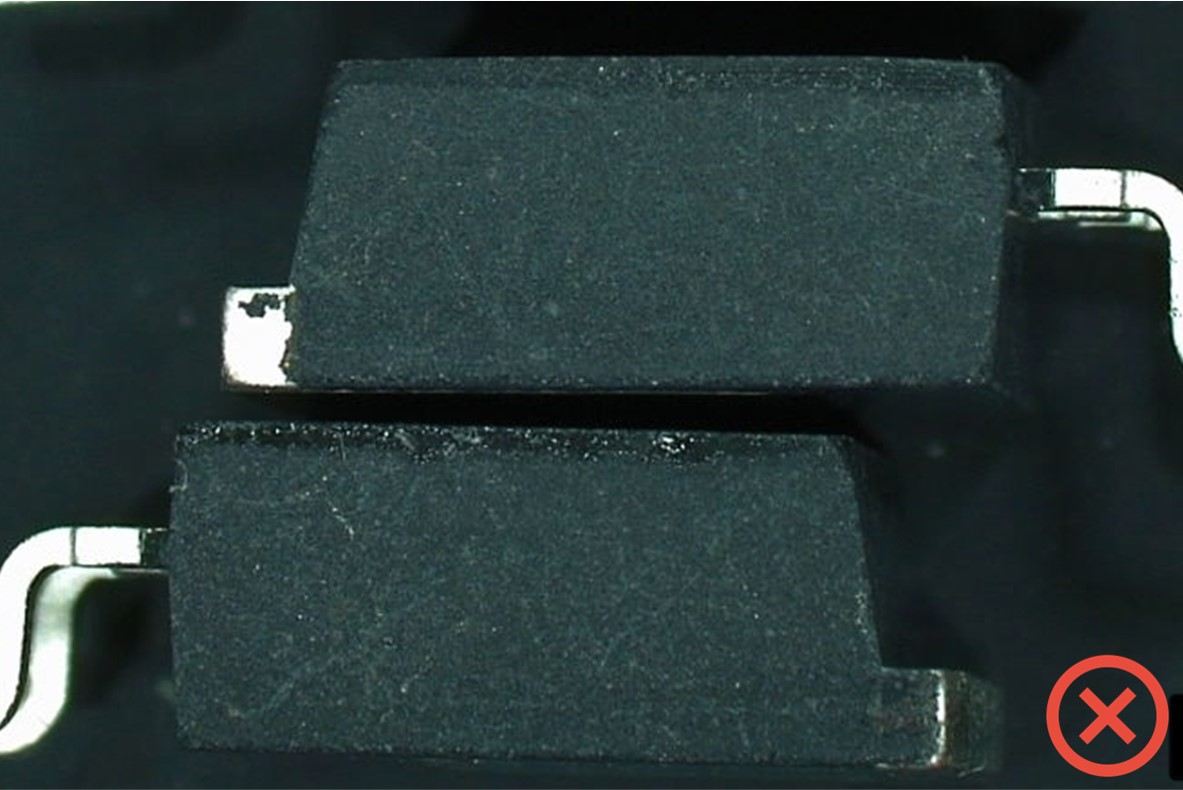
External visual inspection
Marking test
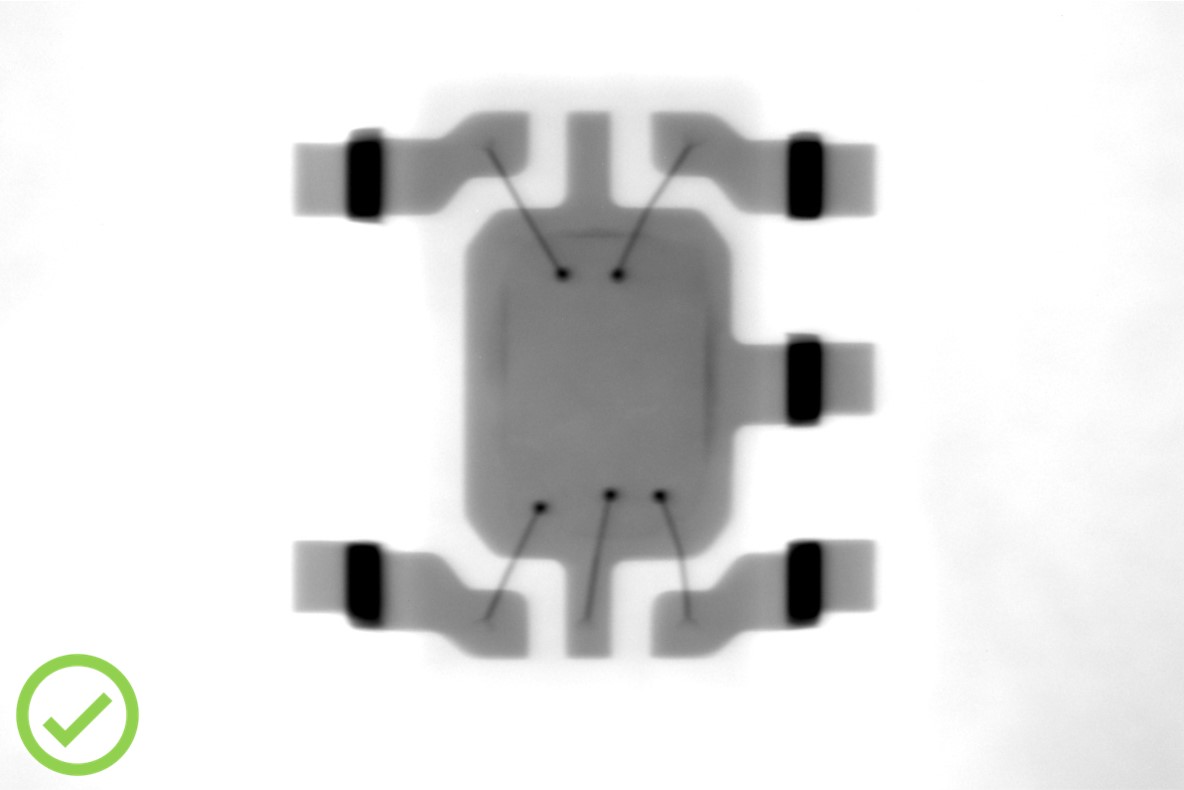
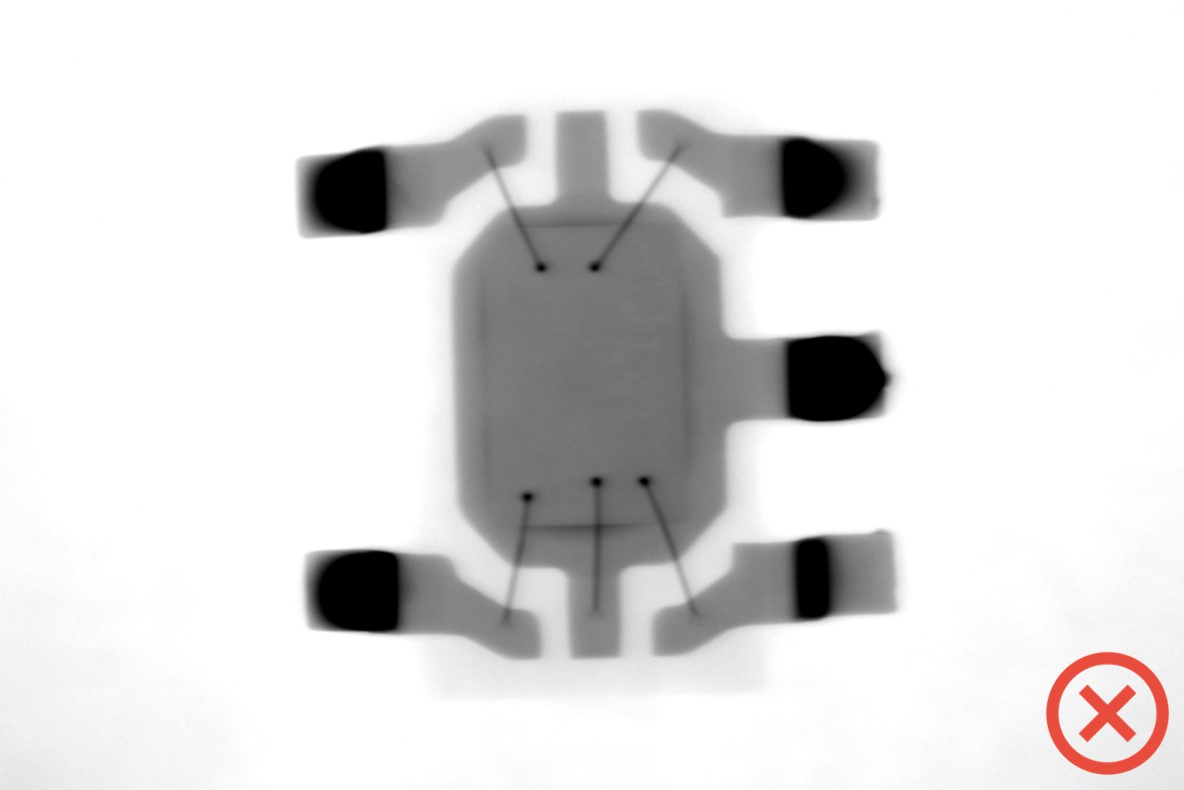
X-ray imaging
Acoustic microscopy
X-ray fluorescence
Electrical test
Solderability
These tests are carried out on all families of electronic components (active, discrete, passive), new or after long-term storage.
Standard tests: counterfeiting detection
Aim: point-out actual counterfeited parts
External visual inspection, marking
MIL-STD-883 Test Method 2009, SCC 24800
Marking test
ESCC 24800
X-ray imaging
MIL-STD-883 Test Method 2012
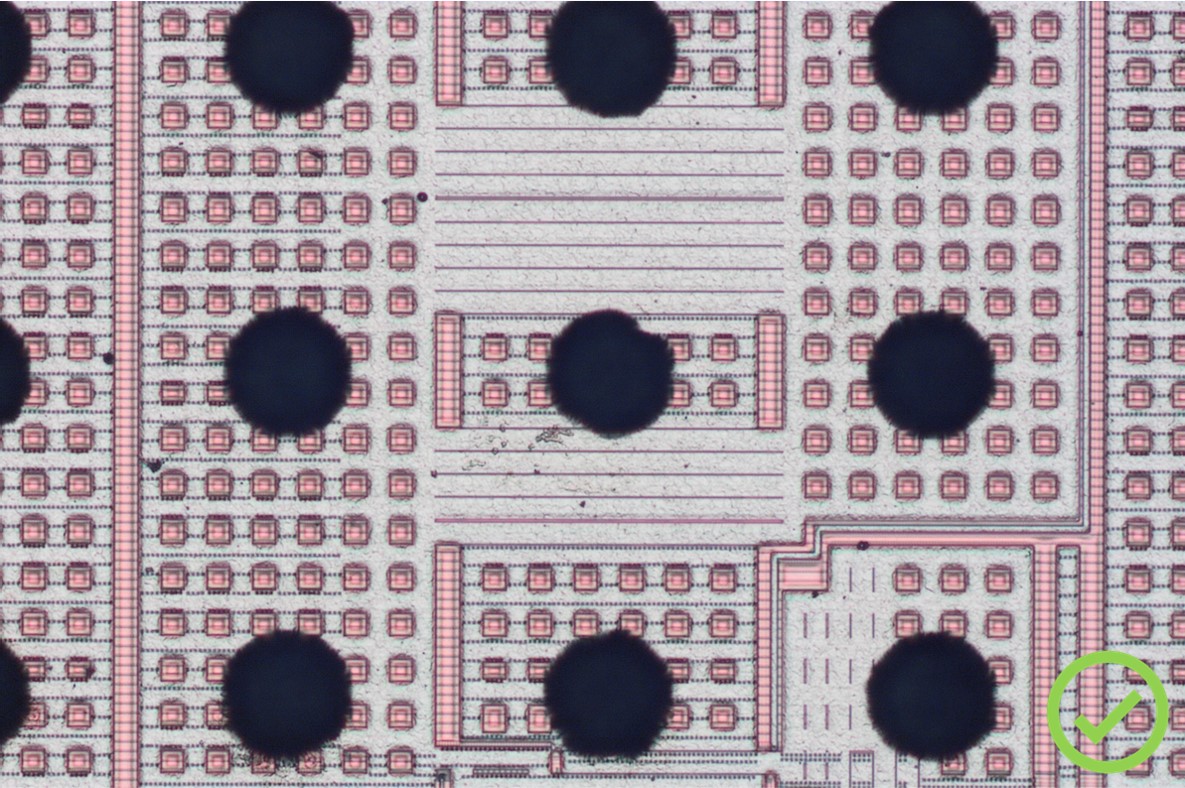
Internal visual inspection after package opening
MIL-STD-883 Test Method 2010
External visual appearance: integrity of the package (marking: typography, punch) and terminations (absence of traces of flux or residual solder indicating a component unsoldered after first use)
Solvent or scalpel test: no sign of blacktopping
Scalpel or solvent (acetone) test: evidence of package remarking
Non-destructive inspection of the elements inside the case: presence of the chip; chip and leadframe dimensions, position and geometry; integrity of interconnections (bondings): diameter, absence of breakage
Correspondence between the serial number of the chip and the one of the package. Comparison with our Components database; absence of anomaly on the chip (connection of bonds, alterations, tool marks, scratches, cracks, stains, traces of corrosion or contamination); passivation layer integrity
Advanced tests : Batch quality and homogeneity
Aim: evaluate the scattering amongst a batch (same date-code) or aging due to long-term storage
Acoustic microscopy (CSAM)
IPC/JEDEC J-STD-035, MIL-883 Method 2030.2
Solderability
IEC-68-2-20 Test Ta Method 1
X-ray fluorescence
Electrical measurements
At room or high temperature
Absence of any critical defect: delamination or crack in the die attach or at the interface between the case and the leadframe / paddle
Observation of the solder wetting region; quality of wettability (good adhesion between the terminations and the solder)
Verification of the termination composition: absence of Lead for RoHS components
Confirmation of electrical characteristics: parametric I(V) or functional tests
Do you want a detailed presentation of our Lab services or consult us about a specific need ?